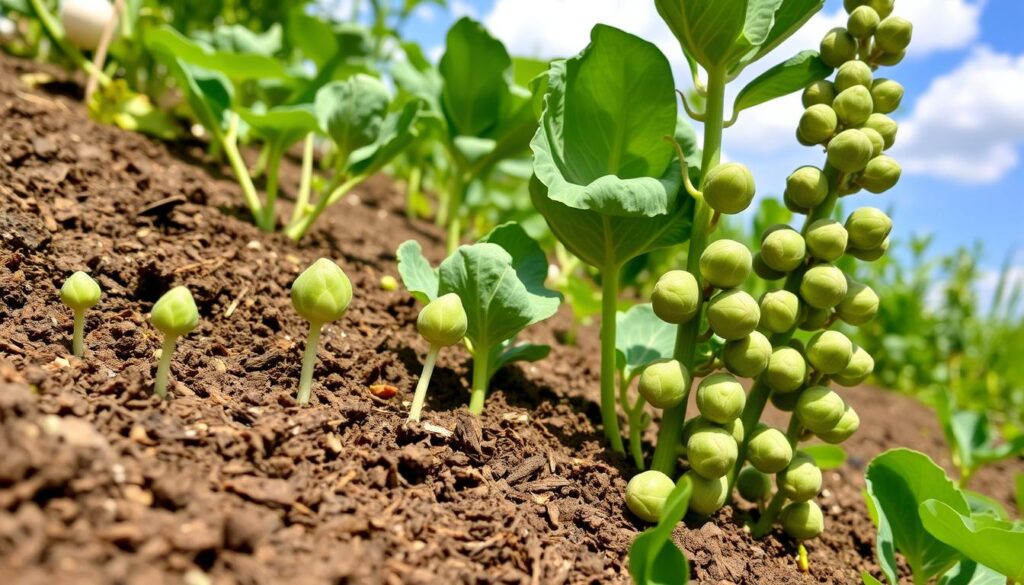
Welcome to our guide on growing Brussels sprouts. It’s rewarding to grow your own. We’ll show you how to go from start to finish.
It’s easy to learn how to grow Brussels sprouts. With patience and dedication, you can grow tasty sprouts at home. We’ll cover soil prep, planting, and care.
Our guide is for everyone, whether you’re new or experienced. It will give you the confidence to grow Brussels sprouts. Let’s start our journey into Brussels sprouts gardening.
Introduction to Growing Brussels Sprouts
We’ll dive into the details of growing Brussels sprouts. You’ll learn the best practices for a great harvest. Our goal is to make growing Brussels sprouts easy and rewarding for you.
Key Takeaways
- Learn the basics of How to Grow Brussels Sprouts with our guide
- Discover the benefits of growing your own Brussels sprouts
- Get tips on soil preparation and planting for a successful harvest
- Understand the importance of proper care and maintenance for your Brussels sprouts plants
- Explore the different varieties of Brussels sprouts and choose the best one for your garden
- Enjoy a bountiful harvest with our expert guidance on How to Grow Brussels Sprouts
Understanding Brussels Sprouts: An Introduction
Brussels sprouts are a cool-season crop from the Brassica family. This family also includes cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower. To grow Brussels sprouts well, knowing their needs is key. Following good growing tips will help you get a big harvest of this healthy veggie.
There are many benefits to growing Brussels sprouts. They are full of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They’re great for a healthy diet. Plus, growing them yourself can be fun and rewarding, letting you enjoy your hard work and connect with nature.
What Are Brussels Sprouts?
Brussels sprouts grow on a stem, looking like small cabbages. They are usually green, but some can be purple or red. To grow them well, they need the right amount of sunlight, water, and nutrients.
Benefits of Growing Your Own Brussels Sprouts
Some benefits of growing your own Brussels sprouts include:
- Freshness: Homegrown Brussels sprouts are always at their best, tasting better and being more nutritious.
- Cost-effectiveness: Growing your own can save you money on grocery bills.
- Customization: You can pick the variety that fits your taste and growing conditions.
Growing Zones and Seasonal Considerations
Brussels sprouts love cool weather and grow best in temperate climates. They do well in many zones, but the best conditions are in cool winters and mild summers. Knowing your area’s specific needs helps your Brussels sprouts grow well, using the right growing tips.
Essential Growing Requirements for Brussels Sprouts
To grow Brussels sprouts well, knowing the key needs is vital. They need lots of sunlight, about 6 hours a day. They also do best in cooler weather, between 60°F and 70°F.
Space needs are also key. Brussels sprouts need about 3 feet of space each to grow right. This helps prevent disease and pests, which can be a problem in crowded gardens.
Here are some important things to think about for a great growing spot for Brussels sprouts:
- Adequate sunlight and temperature control
- Proper spacing and air circulation
- Well-draining soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0
By knowing and meeting these needs, gardeners can have a great harvest. Whether you’re new or experienced, growing Brussels sprouts can be fun and rewarding.
Selecting the Best Soil for Brussels Sprouts
Choosing the right soil is key for growing Brussels sprouts. The soil should have a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. This range is slightly acidic to neutral, perfect for nutrient uptake and disease prevention.
To make the soil ideal, mix in compost, well-rotted manure, and peat moss. These add-ons improve soil structure and water retention. For instance, a 2-inch compost layer boosts fertility and drainage.
Soil Preparation Techniques
- Test the soil pH and adjust it if necessary
- Add organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure
- Mix in peat moss to improve soil structure and water-holding capacity
Good drainage is vital for Brussels sprouts. The soil must drain well to avoid waterlogged conditions. This can cause root rot and diseases. To fix this, add perlite or sand, or use raised beds with a mix of topsoil, compost, and peat moss.
Drainage Considerations
By picking the right soil and preparing it well, gardeners can give Brussels sprouts the best start. With the soil just right, these plants will grow well and yield a lot of tasty sprouts.
| Soil Type | pH Range | Organic Matter |
|---|---|---|
| Clay | 6.0-7.0 | Compost, peat moss |
| Sandy | 6.0-7.0 | Well-rotted manure, perlite |
| Loam | 6.0-7.0 | Compost, peat moss, well-rotted manure |
How to Grow Brussels Sprouts Successfully
Brussels Sprouts Plant Care is key for a great harvest. To grow them well, you need the right conditions. This includes enough water and the right food for the plants.
Some important things to think about for Brussels Sprouts Plant Care are:
- Planting depth: Plant the seeds about 1-2 inches deep to ensure proper germination.
- Watering schedule: Keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged, to promote healthy growth.
- Fertilization: Feed the plants with a balanced fertilizer to promote healthy growth and development.
By following these tips and taking good care of your Brussels Sprouts, you’ll get a big harvest. Remember to keep the soil consistently moist and provide adequate fertilization to ensure the best results.
Planting Methods and Timing
Learning the best ways to plant Brussels sprouts is key for a great harvest. It’s important to know what this crop needs. You’ll have to choose between direct sowing or transplanting.
Direct sowing means planting seeds right in the ground. Transplanting starts seeds indoors and then moves them outside. Each method has its own benefits and drawbacks. Direct sowing is simple and cheap, while transplanting gives seedlings a start.
Direct Sowing vs. Transplanting
Think about your area’s climate and soil when choosing between direct sowing and transplanting. If your growing season is long, direct sowing might be best. But if it’s short, transplanting can help you start sooner.
Spacing Requirements
Spacing is important for Brussels sprouts. Plant them 18-24 inches apart for air and to avoid disease. Rows should be 3 feet apart for easy harvesting.
Best Time to Plant
The best planting time varies by location and climate. Plant in early spring or late summer/early fall, 8 weeks before the first frost. This lets the plants grow before it gets cold. Follow these tips to grow great Brussels sprouts.
- Choose a variety that fights off disease and pests
- Plant in well-draining soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0
- Keep the soil moist but not too wet
Watering and Fertilization Guide
Proper watering and fertilization are key for healthy Brussels sprouts. Understanding the right amount of moisture and nutrients is vital. Brussels sprouts need consistent moisture, more so when they’re producing sprouts.
Water your Brussels sprouts plants deeply once or twice a week, based on the weather. It’s also important to fertilize them regularly. Use a balanced fertilizer to promote healthy growth. Some important Brussels Sprouts Growing Tips for fertilization include:
- Using a fertilizer with a balanced N-P-K ratio
- Applying fertilizer when the plants are about 6 inches tall
- Avoiding over-fertilization, which can harm the plants
By following these Brussels Sprouts Growing Tips and providing the right water and nutrients, you’ll have a successful harvest. Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Fertilize your plants regularly for the best growth.
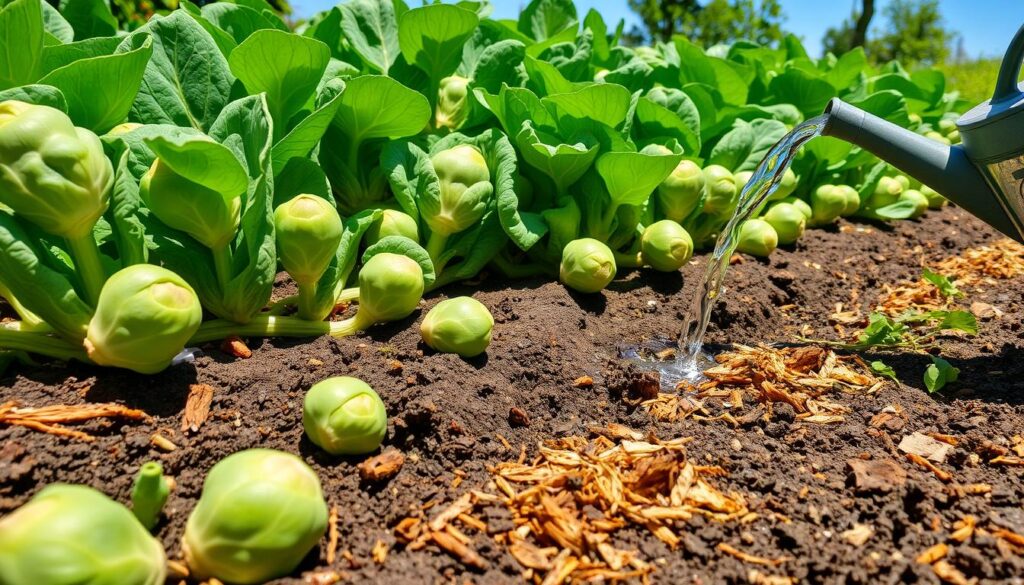

Supporting Your Brussels Sprouts Plants
As your Brussels sprouts plants grow, they need support to stay healthy. Proper Brussels Sprouts Plant Care means giving them the right physical help. This includes staking, protecting from wind, and pruning.
For more info on gardening and plant care, check out container gardening guides. They have tips on supporting your plants.
Staking Methods
Staking is key for Brussels Sprouts Plant Care. It keeps plants upright and prevents them from falling over in the wind. You can use:
- Individual stakes for each plant
- A trellis system for multiple plants
- A cage or teepee to support the plants
Wind Protection
Wind protection is also important for Brussels Sprouts Plant Care. Strong winds can harm plants and lower their yield. To protect your plants, you can:
- Plant them in a sheltered spot
- Use a windbreak, like a fence or trees
- Create a microclimate with a cold frame or hoop house
Managing Common Pests and Diseases
Brussels Sprouts Pests and Diseases can be a big problem for gardeners. It’s important to know the common pests and diseases that harm Brussels sprouts. Aphids, cabbage worms, and flea beetles are common pests. Club root, downy mildew, and powdery mildew are common diseases.
Prevention is key to managing Brussels Sprouts Pests and Diseases. Organic and integrated pest management techniques are helpful. Crop rotation, sanitation, and physical barriers can prevent pests. Also, using disease-resistant varieties can lower disease risk.
Here are some ways to manage common Brussels Sprouts Pests and Diseases:
- Use neem oil to control aphids and other pests
- Apply row covers to prevent cabbage worms and flea beetles from reaching the plants
- Remove infected plants to prevent the spread of disease
- Use copper-based fungicides to control downy mildew and powdery mildew
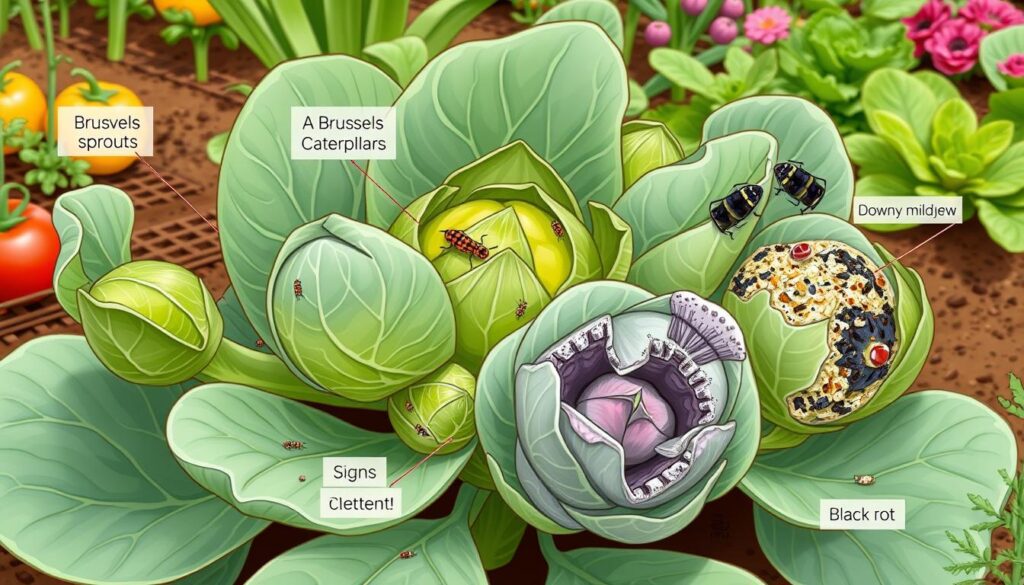
By following these tips and using organic and integrated pest management, gardeners can manage Brussels Sprouts Pests and Diseases. This way, they can enjoy a healthy and productive crop.
| Pest/Disease | Symptoms | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Aphids | Curled or distorted leaves | Neem oil, insecticidal soap |
| Cabbage worms | Holes in leaves, green frass | Row covers, Bt |
| Downy mildew | Yellowing leaves, white powdery growth | Copper-based fungicides, removal of infected plants |
Companion Planting Strategies
Choosing the right companion plants for Brussels sprouts can greatly improve their health and yield. Plants like marigolds can repel nematodes, which harm Brussels sprouts. This is just one example of how companion planting can benefit your garden.
Vegetables like carrots and onions, as well as herbs like sage and rosemary, are excellent companions for Brussels sprouts. They can enhance the health and taste of the sprouts. Yet, some plants should be kept away from Brussels sprouts. For instance, members of the Brassica family, such as broccoli and cauliflower, can be vulnerable to the same diseases.
Here are some tips for companion planting with Brussels sprouts:
- Plant marigolds to repel nematodes
- Use carrots and onions to improve growth and flavor
- Avoid planting members of the Brassica family nearby
Best Companion Plants
Beans, peas, and cucumbers also make great companions for Brussels sprouts. They offer shade, improve soil health, and can serve as a trellis for the sprouts to climb.
Plants to Avoid
It’s best to avoid planting members of the Brassica family near Brussels sprouts. Also, steer clear of plants that compete for water and nutrients, such as tomatoes and peppers.
Harvesting Your Brussels Sprouts
As you near the end of your Brussels sprouts journey, it’s essential to know when and how to harvest your crop. A well-timed harvest is key to enjoying your homegrown Brussels sprouts at their best. The Brussels Sprouts Harvesting Guide suggests checking for sprouts that are firm, green, and about 1-2 inches in diameter.
To determine the best time to harvest, consider the days to maturity listed on the seed package or consult a reliable gardening resource. Generally, Brussels sprouts are ready to harvest about 90-120 days after planting. When harvesting, remove the lowest sprouts first, working your way up the stem. This helps to encourage the plant to continue producing new sprouts.
When to Harvest
Harvesting at the right time is critical to ensure the best flavor and texture. Check your plants regularly, as the sprouts can quickly become overmature and develop a bitter taste.
Proper Harvesting Techniques
To harvest your Brussels sprouts, simply twist or cut the sprouts from the plant, leaving about an inch of stem attached. Be careful not to damage the plant, as this can reduce future yields.
Storage Tips
After harvesting, store your Brussels sprouts in a cool, dry place to preserve their freshness. You can also freeze or can your sprouts to enjoy them year-round. By following these simple steps and using the Brussels Sprouts Harvesting Guide, you’ll be able to enjoy your delicious homegrown Brussels sprouts at their best.

| Harvest Time | Sprout Size | Storage Method |
|---|---|---|
| 90-120 days | 1-2 inches | Refrigerate or freeze |
Extending the Growing Season
Growing Brussels Sprouts in Home Gardens can be challenging due to the short growing season. But, with the right methods, you can make the season longer. Start by using row covers or cold frames to shield your plants from frost.
Here are some ways to extend the growing season:
- Begin your Brussels sprouts seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before the last frost. This gives you a head start.
- Try using season extension methods like hoop houses or greenhouses. They create a warm spot for your plants.
- Plant succession crops every 1-2 weeks. This way, you’ll have a steady supply of Brussels sprouts all season.
By using these methods, you can make the growing season for Brussels sprouts longer. Keep your plants healthy and well-cared for to get the best results.
With a bit of creativity and planning, you can have a big harvest of tasty Brussels sprouts. Even in areas with short growing seasons, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Row Covers | Lightweight fabrics that allow plants to receive sunlight and water while protecting them from frost and freezing temperatures. |
| Cold Frames | Structures that use transparent or translucent materials to cover plants and trap heat, protecting them from frost and freezing temperatures. |
| Season Extension | Techniques used to extend the growing season, such as hoop houses or greenhouses, that create a warm and protected environment for plants. |
Troubleshooting Common Growing Problems
Learning How to Grow Brussels Sprouts means knowing about common issues. Pests and diseases can harm your plants. Spotting problems early helps prevent damage and ensures a good harvest.
Leaf Issues
Yellow or curled leaves can be due to pests, diseases, or lack of nutrients. Regular checks and quick action are key. Common leaf problems include:
- Aphid infestations
- Whitefly damage
- Fungal diseases
Growth Problems
Stunted or deformed plants can be due to poor soil, too little water, or too much heat. Good soil, enough water, and support are essential. This helps your plants grow well.
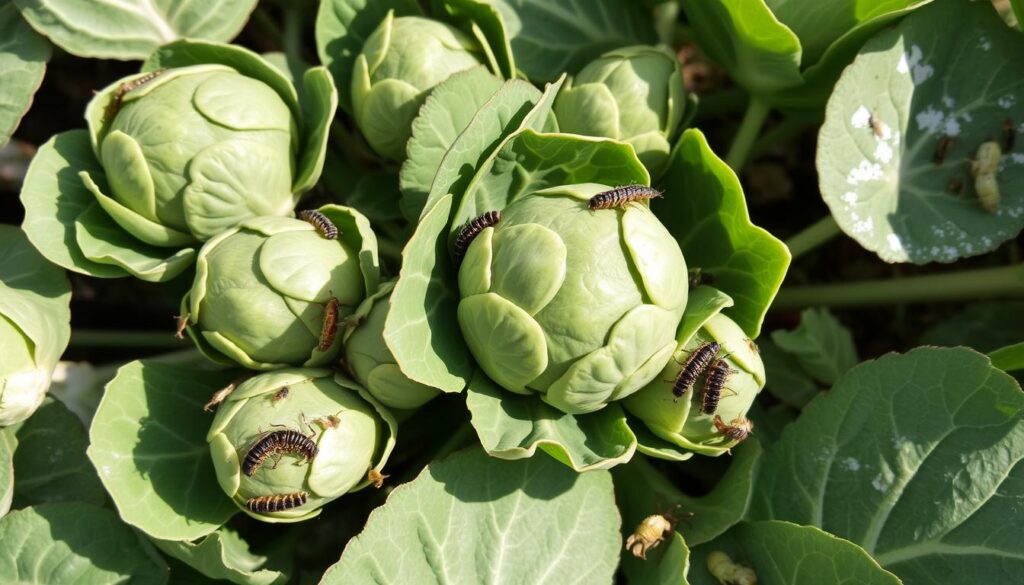

Sprout Quality Concerns
Small or misshapen sprouts can be fixed with the right growing conditions. Make sure your plants get enough light, water, and nutrients. With these tips, you’ll have a great harvest of healthy Brussels sprouts.
Conclusion: Growing Success with Brussels Sprouts
Growing delicious Brussels sprouts requires patience and a willingness to learn. By following the steps in this guide, you’re ready to grow a thriving crop in your garden. You’ll learn about the plant’s needs, how to manage pests, and diseases.
Every garden is different, so be ready to make adjustments. Watch your plants closely, note your successes and challenges, and keep learning. With proper care, you’ll enjoy a harvest of tasty, nutritious Brussels sprouts.
Start your Brussels sprouts growing journey and explore other gardening topics too. Growing your own food is rewarding and can lead to many more gardening adventures. Happy growing!
FAQ
What are the ideal growing conditions for Brussels sprouts?
Brussels sprouts love cool, temperate weather and well-drained soil. They need full sun and regular water. This helps them grow well.
When is the best time to plant Brussels sprouts?
Plant Brussels sprouts in spring or early summer. The exact time depends on your area. In most places, plant 4-6 weeks before the last frost.
How do I prepare the soil for planting Brussels sprouts?
Add compost or manure to the soil to make it better. Brussels sprouts like slightly acidic soil, pH 6.0-7.0. Make sure the soil is loose for roots to grow.
How far apart should I space Brussels sprouts plants?
Plant Brussels sprouts 18-24 inches apart. Rows should be 2-3 feet apart. This space helps them grow well.
How do I care for my Brussels sprouts plants?
Keep them watered, fertilized, and pruned. Water deeply, 1-2 inches a week. Feed them every 4-6 weeks. Prune lower leaves for better air and sprouts.
What are some common pests and diseases that affect Brussels sprouts?
Aphids, cabbage worms, and cabbage loopers are pests. Black rot, clubroot, and downy mildew are diseases. Use good hygiene, row covers, and organic methods to fight them.
When should I harvest my Brussels sprouts?
Harvest Brussels sprouts 80-90 days after transplanting. They’re ready when 1-2 inches and firm. Start with the lower sprouts.
How do I store and preserve my harvested Brussels sprouts?
Store them in the fridge in a bag or container for a week. Freeze them by blanching first. You can also can or ferment them.

